Cosmologia
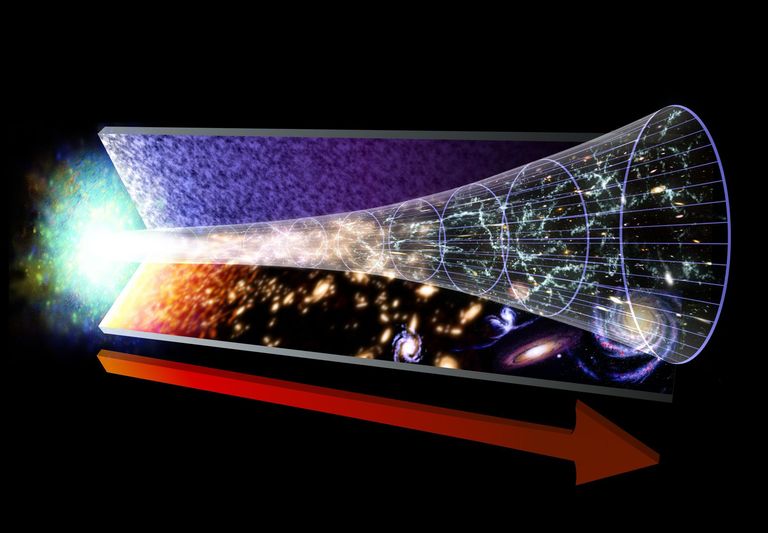
Mentre l'astronomia studia oggetti concreti nello spazio, come le stelle o le comete, la cosmologia esplora la struttura dell'universo. Essa cerca di spiegare come è nato il nostro universo, come si è sviluppato e quali sono le forze fisiche e le leggi fondamentali che lo regolano. Oggi la maggior parte dei-lle cosmologi-ghe si basa sulla teoria del Big Bang, il cosiddetto modello standard della cosmologia: Dopo il Big Bang, avvenuto circa 13,8 miliardi di anni fa, il nostro universo si è espanso da uno stato estremamente denso con temperature elevate, dando origine allo spazio, al tempo e alla materia. Dopo aver attraversato diverse fasi, ha assunto la sua forma attuale.
La cosmologia studia la gamma più estrema di grandezze: dalle forze che agiscono tra le particelle elementari, come gli elettroni, alle forze tra le galassie. Per le scale più piccole, i-le ricercatori-trici ricorrono alla fisica quantistica. Per le macroscale, la teoria della relatività generale spiega l'interazione degli oggetti nello spazio e nel tempo. Per comprendere la struttura del nostro universo, sono ad esempio importanti i buchi neri.




